Between the hours of 10:25pm on Monday 16th April and 05:10am on Thursday 19th April the UK went coal free. During this 55 hour time period the power stations in the UK used no coal to generate electricity. This is a great leap forwards in the shift towards cleaner, greener power sources for the UK.
The last time the UK went this long without coal was 136 years ago.
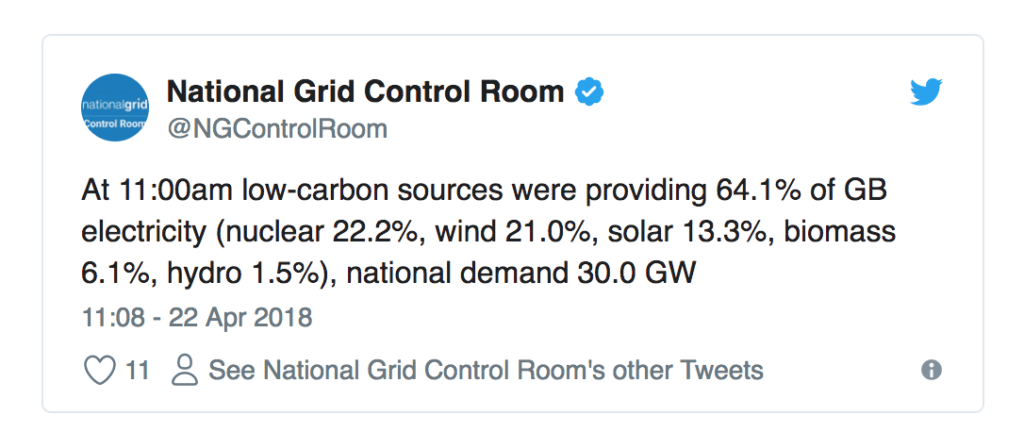
Alternative energy sources are already starting to take more of a roll in providing energy to the UK. There is a wide range of alternative energy sources that are now being used in the UK, which include:
Wind power
The UK has great conditions to generate electricity from wind, as it has high average wind speeds. The UK has invested in both onshore and offshore wind farms. The UK has installed as much wind power capacity as the rest of the world combined.
Bioenergy
Biomass, which can come from any living thing, along with biodegradable waste like food, can be burnt in thermal power and heat generation. The gas from bioenergy can also be injected into the gas grid, in the form of refined methane, which is a byproduct that occurs when bio matter is broken down.
Marine, wave and hydroelectricity
The flow of water is used to turn turbines to generate electricity. There are different types of hyrdo power, which cover dam storages and the flow of the river. Marine technologies are expected to make a significant contribution to renewable power generation after 2020.
Solar PV
Solar PV (photovoltaics) are panels that convert the rays of the sun into energy. Current installed capacity exceeds 8.7GW and is increasing rapidly, with year-on-year growth exceeding 80% in 2015.
The UK is moving towards decarbonising its energy:
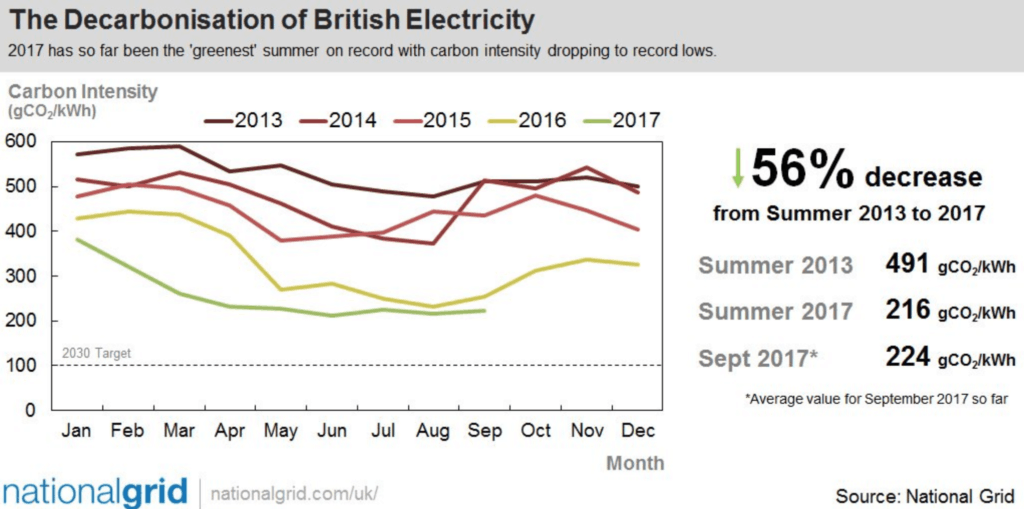
Why Coal is so bad?
.
- Coal is not renewable. There is a finite supply, which is being depleted
- Coal contains the most CO2 per BTU, the largest contributor to global warming
- High cost of transporting coal to centralised power plants
- Coal ash is a hazard and a disposal problem
- Coal burning releases SOx and NOx which both can cause acid rain
- Burning coal emits mercury and other heavy metals that pose a significant health risk
- Coal emissions linked to increased rates of asthma and lung cancer
What about our stoves?
The stoves sold in the Charlton & Jenrick range are all multi-fuel, which means you can use coal, and of course, wood. Although we always like to provide a choice for our customers, and wood may not always be available, we would always recommend using wood for regular stove use. Burning wood over coal has many advantages, which include:
.
- Wood is a sustainable energy source
- Efficiently burning wood can be carbon neutral
- Correctly seasoned wood is much cleaner than coal
How is wood carbon neutral? CO2 is taken out of the atmosphere by the growth of trees, at the same rate CO2 is created by the burning of wood. This is effectually a closed CO2 cycle. The CO2 impact from burning wood is offset with the growth of new trees. This alone is a compelling reason why burning wood is so much better than coal.
You are able to learn more about UK national energy at The National Grid website – https://www.nationalgrid.com/








